Electric Cars: Unveiling the Technology Behind the Green Revolution
How Do Electric Cars Work: A Deep Dive into EV Technology
So, you're curious about electric cars? You're not alone! They're becoming increasingly popular, and it's easy to see why: they're quiet, efficient, and environmentally friendly. But how *exactly* do they work? Let's take a look under the hood (or should we say, under the… well, you get it!).
The Heart of the Matter: The Battery
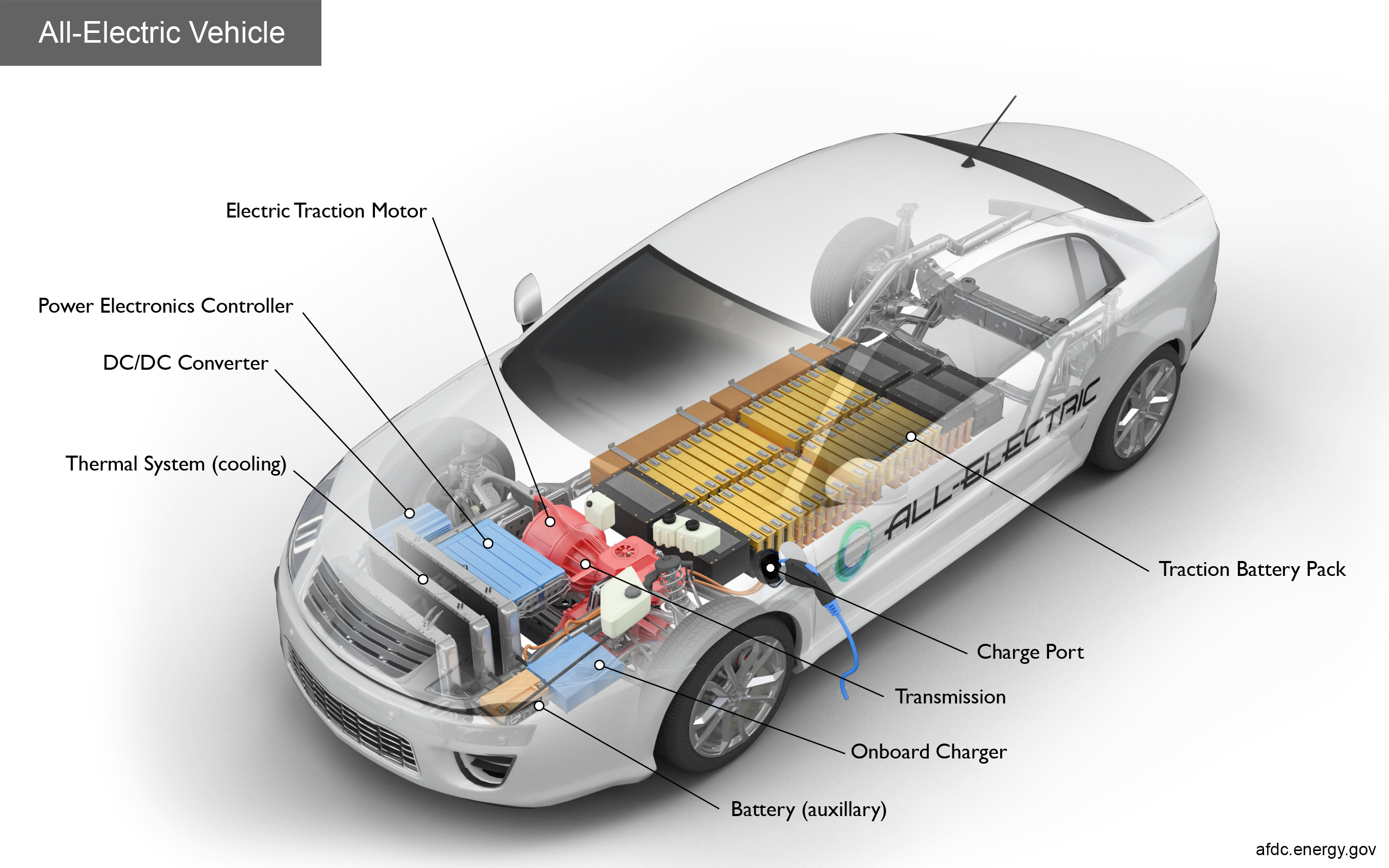
The most crucial component of any electric car is its battery. Think of it as the car's fuel tank, but instead of gasoline, it stores electrical energy. Most EVs use lithium-ion batteries, the same technology found in your smartphone or laptop. These batteries are made up of thousands of individual cells, each storing a small amount of electricity. When connected together, they pack a serious punch, providing the power needed to propel the car.
But how does the battery actually *store* energy? It's a bit complicated, but basically, it involves the movement of lithium ions between two electrodes (a positive cathode and a negative anode) through an electrolyte. When you need power, the ions flow back and forth, creating an electrical current. The more cells you have, the more energy you can store – and the further you can drive.
From Battery to Wheels: The Motor and Inverter
Once the battery is charged, it's ready to unleash its power. But the electricity doesn't go straight to the wheels. It first passes through an inverter. This clever device acts as a translator, changing the direct current (DC) electricity from the battery into alternating current (AC) electricity. Why? Because AC is what electric motors need to run.
The electric motor itself is surprisingly simple compared to a gasoline engine. It has no pistons, no spark plugs, no complicated combustion process. It uses electromagnetism to create rotational force. In short, electricity creates a magnetic field, which interacts with another magnetic field, causing the motor to spin. This rotation then turns the car's wheels via a transmission system (though some EVs have single-speed transmissions, streamlining the process).
How Do Electric Cars Work: Regenerative Braking – The Smart Saver
One of the coolest things about electric cars is regenerative braking. Ever noticed how some EVs seem to coast more efficiently when you release the accelerator? That's regenerative braking in action! When you lift your foot off the accelerator, the motor acts as a generator, converting the car's kinetic energy (motion) back into electricity. This electricity is then fed back into the battery, effectively extending your driving range. It's like recharging your battery while you're braking – super efficient!
Charging Up: Powering Your EV
Charging an electric car is different from filling up a gas tank. You plug it in, just like charging your phone! However, there are different levels of charging. Level 1 charging is simply plugging into a standard household outlet, which is slow but convenient. Level 2 charging uses a dedicated charging station, delivering a much faster charge. And then there's DC fast charging, which can significantly top up your battery in a relatively short time. The charging time depends on the car's battery capacity and the charging level.
How Do Electric Cars Work: The Components and their Interaction
Let's recap the core components and their beautiful interplay. The battery stores the electrical energy. The inverter converts the DC electricity from the battery to the AC electricity the motor needs. The motor converts this electrical energy into rotational motion, turning the wheels. And finally, regenerative braking converts kinetic energy back into electricity, boosting efficiency. It's a system working in remarkable harmony!
Advantages of Electric Vehicles
Beyond the fascinating technology, electric cars offer numerous benefits. They produce zero tailpipe emissions, contributing to cleaner air and a smaller carbon footprint. They're often cheaper to operate, with lower maintenance costs and electricity usually being less expensive than gasoline. And let's not forget the quiet and smooth driving experience – a true joy for the senses!
How Do Electric Cars Work: Addressing Common Concerns
Many people have questions and concerns about EVs. Let's address some common ones:
Range Anxiety:
Yes, range anxiety – the fear of running out of charge – is a legitimate concern for some. However, battery technology is rapidly improving, and modern EVs offer impressive ranges. Careful planning, utilizing navigation systems that account for charging stops, and understanding your car's range can mitigate this concern significantly.
Charging Infrastructure:
The availability of charging stations is improving constantly, especially in urban areas. However, in more remote regions, charging infrastructure may still be limited. Planning your journeys carefully is still key for now.
Charging Time:
Charging times vary depending on the charging method. While Level 1 charging is slow, Level 2 and DC fast charging offer much shorter charging times, making it less disruptive to your routine.
Battery Lifespan:
EV batteries have a limited lifespan, but they typically last for many years and thousands of miles. Most manufacturers offer warranties to cover battery degradation.
Cost:
The initial purchase price of an electric car can be higher than a comparable gasoline-powered vehicle. However, government incentives, lower running costs, and potential savings on maintenance can offset this initial investment over time.
Conclusion
Electric cars are more than just a trend; they represent a significant shift in automotive technology. Understanding how they work, from the battery's intricate chemistry to the seamless interaction of its components, helps us appreciate their sophistication and potential. As technology continues to evolve, electric vehicles are poised to play an increasingly crucial role in shaping a sustainable transportation future. They're not just a different way to get around; they're a smarter, greener way forward.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: How long does it take to charge an electric car?
A1: Charging time varies greatly depending on the battery size, charging infrastructure, and charging level (Level 1, Level 2, or DC fast charging). It could range from a few hours to several minutes.
Q2: How far can an electric car travel on a single charge?
A2: The range varies significantly depending on the car model, battery size, driving style, weather conditions, and other factors. Ranges can now extend to over 300 miles on a single charge for many models.
Q3: Are electric cars more expensive to maintain than gasoline cars?
A3: Generally, electric cars have lower maintenance costs due to fewer moving parts and less frequent oil changes.
Q4: Are electric car batteries recyclable?
A4: Yes, electric car batteries are recyclable, and recycling programs are being developed to recover valuable materials and minimize environmental impact.
Q5: How do electric cars perform in cold weather?
A5: Cold weather can affect the range of electric cars. However, modern EVs often have battery heating systems to mitigate this effect.
